Enable fTPM In Windows PC: A Step-by-Step Guide 2024
fTPM will be a super important feature for Windows users in 2025.

Microsoft recently announced that 14th October 2025 will be the Windows 10 support end date.
To this date, Microsoft will be providing necessary security updates for Windows 10. Beyond this date, Windows users have to consider upgrading their Windows version to Windows 11.
But your PC must have TPM 2.0 installed.
What is TPM 2.0?
It is the latest version of the Trusted Platform Module which is a specialized security chip embedded in a computer’s motherboard.
But there are various types of TPMs. One such type is fTPM.
But before getting into what is fTPM and how to enable it, it is important to be clear about what TPM is, what are the different types of TPMs, how it works and its importance in Windows 11 devices.
What Is TPM?
TPM or Trusted Platform Module is a small dedicated chip found in many modern computer motherboards. It enhances the security of a device by encrypting and protecting the data stored in the drive.
If someone tries to change the operating system or firmware, the TPM can detect this and prevent the computer from booting up.
How Does TPM Work?
When you encrypt files or data on your computer, the TPM generates and stores the keys needed to unlock that data. This means that if someone steals your hard drive, they can’t access your files without the correct key.
When you turn on your computer, the TPM checks that everything is in order before the operating system loads. If it detects any unauthorized changes, it can stop the boot process to protect your data.
What Are The Different Versions Of TPM?
There are 2 versions of TPMs
- TPM 1.2:
TPM 1.2 uses SHA-1 and RSA algorithms and supports AES 128-bit encryption optionally. It is supported by Windows 7/8/8.1/10, RHEL, and Ubuntu. It lacks cryptographic key capabilities. TPM 1.2 devices can have EK certificates pre-installed - TPM 2.0:
TPM 2.0 supports newer algorithms like SHA-256, ECC P-256, and ECC BN-256 along with RSA. So TPM 2.0 is more secure and flexible. It also supports AES 128-bit encryption. TPM 2.0 is supported by Windows 8/8.1/10/11, RHEL, and Ubuntu. TPM 2.0 provides better security using advanced cryptographic key capabilities like RSA and ECDSA encryption/signing. It has separate functionality for signing/attestation (EK) and encryption (SRK). The firmware-based TPM 2.0 requires EK certificates to be installed separately.
In this article, we are concerned only with the latest version of the Trusted Platform Module i.e. TPM 2.0.
What Are The Different Types Of TPM 2.0?
Types of TPM 2.0
- Discrete TPM (dTPM): This is a physical chip that sits on the motherboard. It provides strong security to your device and is very safe as it is hard to tamper.
- Firmware TPM (fTPM): This type is a firmware-based TPM, usually built into the CPU. While it provides security, it’s not as secure as a discrete TPM because it shares resources with the main processor. It is usually found in smaller, cost-effective devices.
- Integrated TPM (iTPM): This is similar to fTPM but includes extra security features. It combines TPM functions with other parts of the processor, helping the device to balance performance along with safety.
- Virtual TPM (vTPM): Used in virtual machines and cloud environments, vTPMs are created by software that manages virtual systems. They allow secure operations when a physical TPM isn’t available.
- Software-based TPM: This type mimics TPM functions using software instead of hardware. It’s not as secure as hardware-based TPMs and can be more easily attacked.
Importance Of TPM 2.0 In Windows 11
Microsoft took a revolutionary step by making TPM 2.0 a mandatory requirement for Windows 11 installation. This decision highlights its importance in achieving the company’s security goals for the operating system.
Why TPM 2.0 Is Necessary For Windows 11 Installation
- 2 of the most important system requirements for Windows 11 installation are TPM 2.0 and Secure Boot. TPM along with Secure Boot works together to provide a secure environment for the users by reducing the risk of unauthorized access, making it harder for hackers to compromise the system.
- TPM 2.0 which is an integral part of Secure Boot ensures the system only boots with software trusted by the manufacturer.
- They also prevent malware and unauthorized software from loading during the startup process.
- With the help of the security feature of TPM 2.0, Windows 11 uses its BitLocker feature to create a strong encrypted environment to safeguard the data and files on the device drive.
- TPM 2.0 provides more security enhancement to Windows Hello, which is a biometric authentication system for Windows 11 devices.
- 2 of the most important system requirements for Windows 11 installation are TPM 2.0 and Secure Boot. TPM along with Secure Boot works together to provide a secure environment for the users by reducing the risk of unauthorized access, making it harder for hackers to compromise the system.
- TPM 2.0 which is an integral part of Secure Boot ensures the system only boots with software trusted by the manufacturer.
- They also prevent malware and unauthorized software from loading during the startup process.
- With the help of the security feature of TPM 2.0, Windows 11 uses its BitLocker feature to create a strong encrypted environment to safeguard the data and files on the device drive.
- TPM 2.0 provides more security enhancement to Windows Hello, which is a biometric authentication system for Windows 11 devices.
- TPM 2.0 helps prevent firmware attacks by ensuring that the firmware is authentic and hasn’t been tampered with. This is crucial for protecting the lower levels of a system’s architecture, which traditional antivirus solutions may not reach.
What is fTPM?
fTPM is a firmware-based Trusted Platform Module found embedded in modern CPUs.
Unlike dTPM which relies on a separate hardware chip, fTPM is integrated into the processor’s firmware. This means that the security functions such as securely storing encryption keys and enabling secure boot are now managed by the processor itself.
Both AMD and Intel offer fTPM in their recent processors. AMD sticks with the name “fTPM,” while Intel refers to their version as “Platform Trust Technology” (PTT).
How To Check fTPM 2.0 On Your PC
Windows 10 users who want to upgrade their PCs to Windows 11 must enable TPM 2.0 on their devices.
Most PCs manufactured in the last 5 years have TPM 2.0 enabled by default.
But, if you are using PCs older than 5 years, then you may have older TPM 1.2 instead of TPM 2.0.
Before taking any buying decisions you must first check whether your PC supports fTPM or not.
How To Check fTPM On Your PC
- Check for Windows 11 Compatibility
fTPM is one type of TPM 2.0. It is one of the most important system requirements for running Windows 11 on your PC as well.
To check Windows 11 compatibility we use the PC Health Check app. When we run the Windows 11 compatibility check on this app, it shows the status of your TPM 2.0. If your processor has no TPM 2.0, it will show “TPM not detected” and “TPM 2.0 must be supported and enabled on the PC“.
- Check Your Processor
If you have an Intel processor, check your processor in the list of fTPM-supported Intel processors.
If you have an AMD processor, then check your processor in the list of fTPM-supported AMD processors.
- Check in the TPM Management Tool
Open the Run dialog box by pressing the Windows key and the “R” key together. Then type tpm.msc, and press Enter. If you have TPM installed on your device it will show the TPM version under TPM Manufacturer Information.
If you are using an FTPM-supported processor or device and still PC Health Check shows your device is incompatible, then probably you may have to enable fTPM on your PC.
How To Enable fTPM On Your PC
There are two methods following which you can enable fTPM on your device.
How To Enable fTPM From BIOS Settings
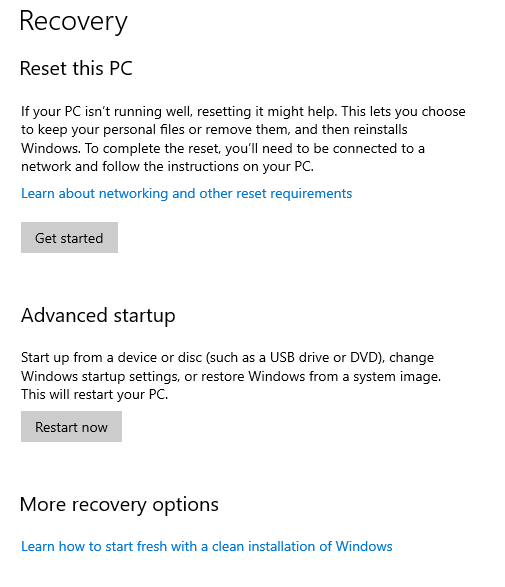
- Right-click on the Windows Start button and then choose “Settings.”
- Click on “Update and Security.”
- From the left sidebar choose “Recovery.”
- Then choose “Advanced Startup.”
- Then the system will prompt you to restart your device.
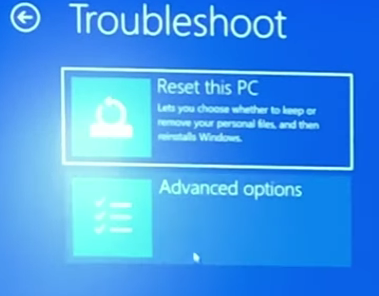
- After reboot it will prompt you to select one of the options. Choose “Troubleshoot.”
- Then click on “Advanced Options.”
- TPM 2.0 needs a modern UEFI Bios environment to work. It cannot work in legacy BIOS. So you have to choose “UEFI Firmware Settings.”
- Then click on “Restart.”
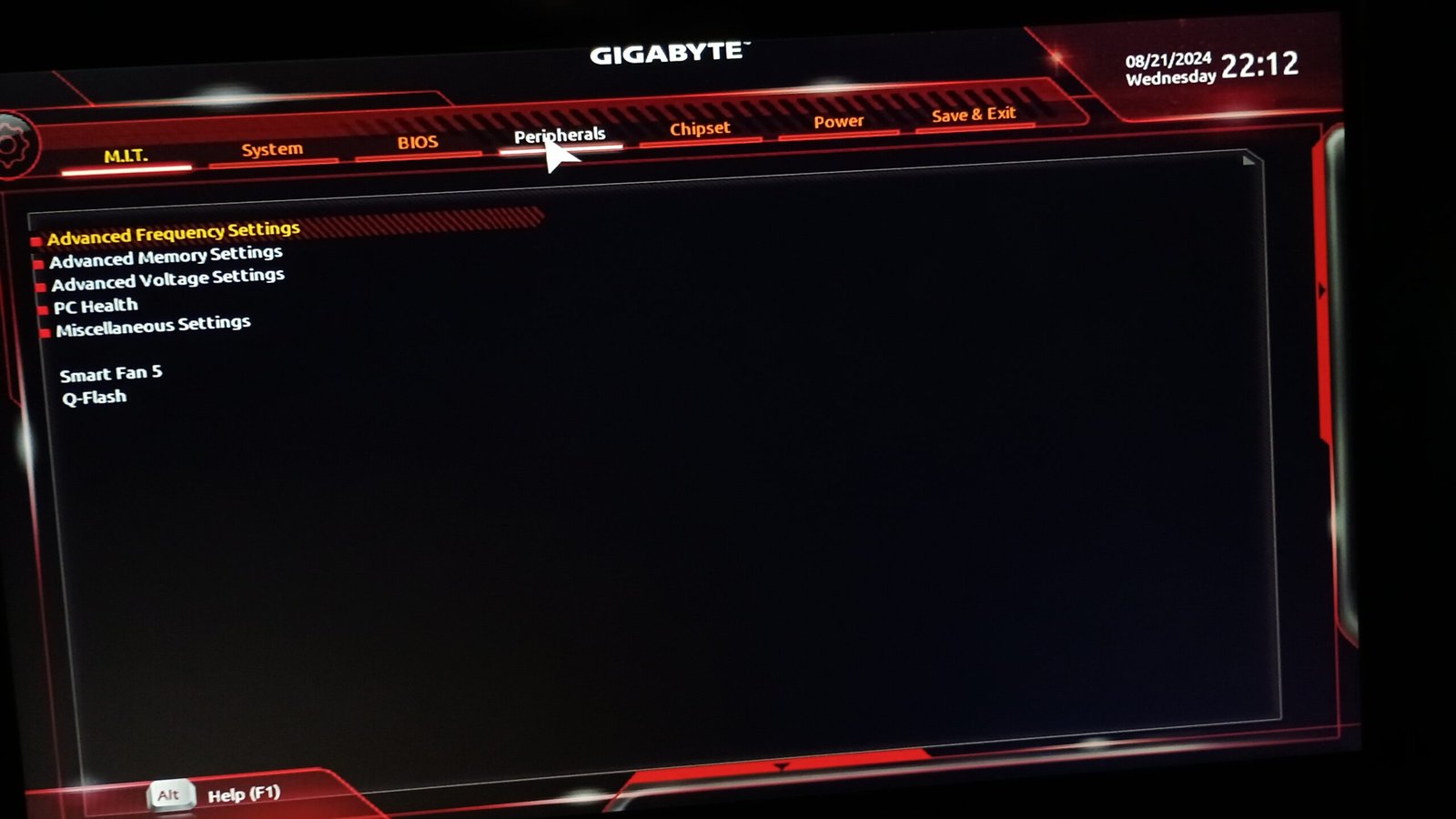
- Before reboot enter BIOS.
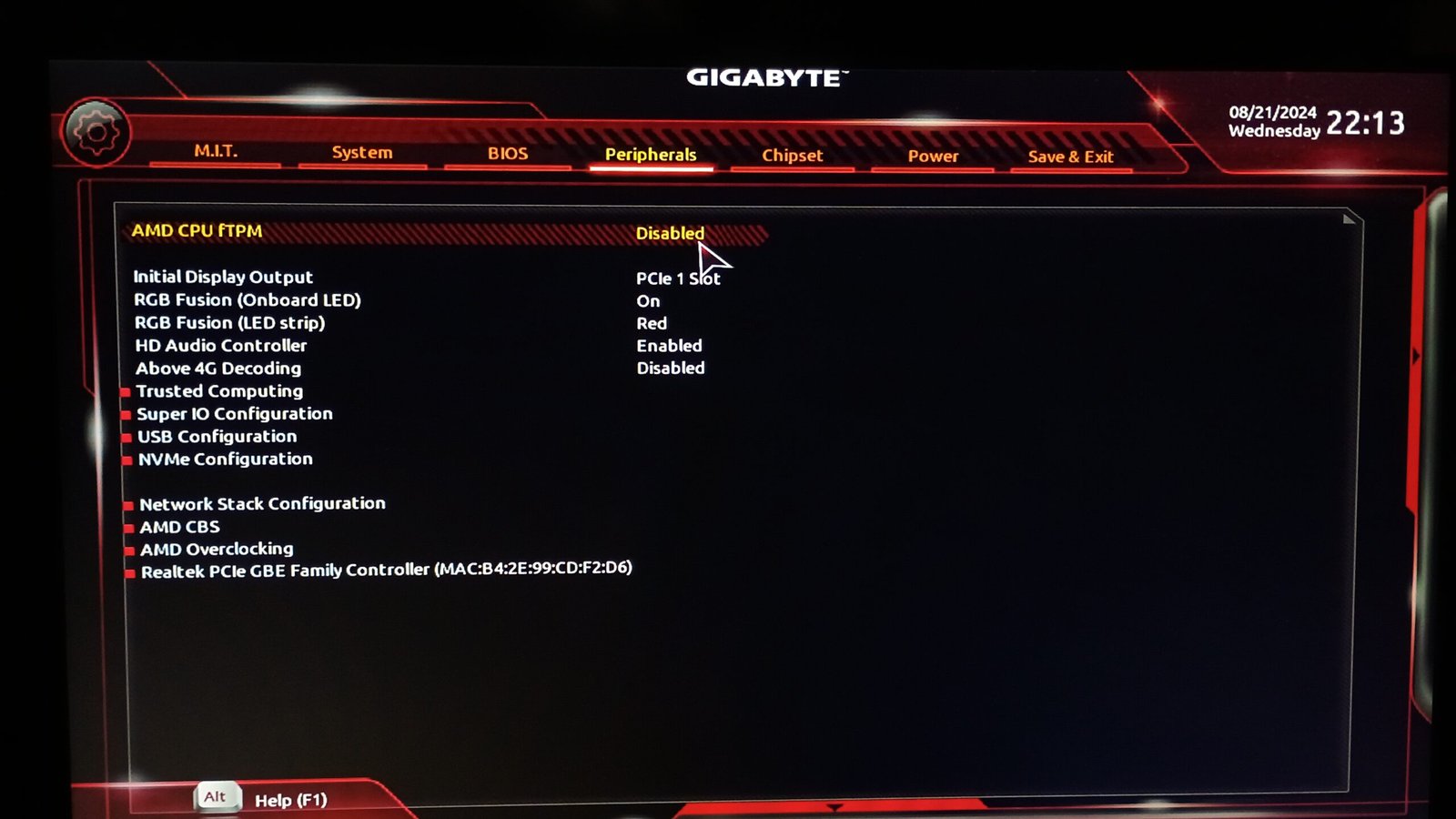
- fTPM enable and disable options can vary from motherboard to motherboard. For example, in the Gigabyte BIOS setup, you can find fTPM enable and disable option under the “Peripheral” tab whereas in the MSI BIOS, you can find the same in Settings>Security>Trusted Computing.
- After enabling fTPM, remember to save and then exit.



How To Manually Add fTPM In Device Manager
- Search “Device Manager” in the Windows Search bar.
- Open “Device Manager.”
- Click on “Actions” on the top bar of the “Device Manager” window.
- From the drop-down menu select “Add Legacy Hardware.”
- Then accept the prompt to click “Next.”
- Then check the option “Install the hardware that I manually select from a list” and click on “Next.”
- From the list of common hardware types search “Security Devices” and then double-click on it.
- From the manufacturer section select “Standard” and then click “Next.”
- Go back to the device list of the “Device Manager.”
- If you can’t see the newly installed TPM 2.0 in your security device then click on “View” and select “Show hidden devices.”
- Expand “Security Devices” to find Trusted Platform Module 2.0.
- Double click on the TPM security device.
- TPM properties window will appear. Click on update drivers to update the firmware to its latest version.
Why Disable fTPM?
Both Intel and AMD had developed their firmware-based TPM 2.0 or fTPM to provide their users with a layer of security within their chipset without having to purchase a separate hardware-based TPM module or dTPM.
But the fTPM carries some disadvantages with it which I have listed below.
Disadvantages of fTPM in Windows PC
- Performance Issues
Some users especially AMD Ryzen users are facing random stutter while running Windows. They also suffered a performance drop while gaming or running resource-hungry software or programs. - Less Secure
fTPM is a firmware-based TPM integrated into the CPU of your PC. Thus it sometimes proves to be less secure than dTPM (Discrete TPM) which is a physically separate hardware. - Incompatibility with Some Software
Some applications or drivers may not work well with fTPM, leading to unexpected behaviour or crashes. - Requires BIOS Support
As I have discussed earlier that fTPM can be enabled or disabled using BIOS settings. So the proper functioning of fTPM depends on the BIOS of a PC. If the BIOS is outdated or does not fully support fTPM, users may experience crashes or slow performance. - Difficult to Diagnose Problems
Troubleshooting any problem relating to fTPM is a challenging task for users who maybe not so tech-savvy.
FAQs
Is it safe to disable fTPM in Windows 11 PC?
It is generally safe to disable firmware TPM (fTPM) on a Windows PC, especially if you are not actively using any TPM-dependent features like BitLocker encryption or Windows Hello.
Is it safe to reset fTPM in Windows PC?
If your system is configured to use TPM for secure boot or other security features, resetting fTPM may lead to boot problems, especially if you have made recent hardware changes.
What is the “Press Y to Reset fTPM” message?
If you encounter a message asking you to press “Y” to reset fTPM during boot, it means your system detected a change in the CPU or motherboard. If you have BitLocker encryption enabled, find your BitLocker key before resetting fTPM. If BitLocker not enabled then you can safely reset your fTPM.